Chikungunya
What is Chikungunya?
Chikungunya (pronunciation: \chik-en-gun-ye) virus is transmitted to people by mosquitoes. The most common symptoms of chikungunya virus infection are fever and joint pain. Other symptoms may include headache, muscle pain, joint swelling, or rash. Outbreaks have occurred in countries in Africa, Asia, Europe, and the Indian and Pacific Oceans. In late 2013, chikungunya virus was found for the first time in the Americas on islands in the Caribbean.
There is a risk that the virus will be imported to new areas by infected travelers. There is no vaccine to prevent or medicine to treat chikungunya virus infection. Travelers can protect themselves by preventing mosquito bites. When traveling to countries with chikungunya virus, use insect repellent, wear long sleeves and pants, and stay in places with air conditioning or that use window and door screens.
Treatment
- There are no antiviral medicines to treat chikungunya
- There are medicines to help reduce the fever and pain
Illness course and outcomes
- Most patients feel better within a week
- Some people may develop longer-term joint pain
- People at increased risk for severe disease include newborns exposed during delivery, older adults (≥65 years), and people with medical conditions such as high blood pressure, diabetes, or heart disease
- Deaths are rare
Prevention
- There is no vaccine or medication to prevent chikungunya virus infection or disease
- Reduce mosquito exposure
- Use air conditioning or window/door screens
- Use mosquito repellents on exposed skin. Repellents containing DEET, picaridin, IR3535, and some oil of lemon eucalyptus and para-menthane-diol products provide long lasting protection.
- Wear long-sleeved shirts and long pants
- Wear permethrin-treated clothing
- Empty standing water from outdoor containers
- Support local vector control programs
- People at increased risk for severe disease should consider not traveling to areas with ongoing chikungunya
Outbreaks
- If you are sick with chikungunya, avoiding mosquito bites will help prevent further spread of the virus
The disease
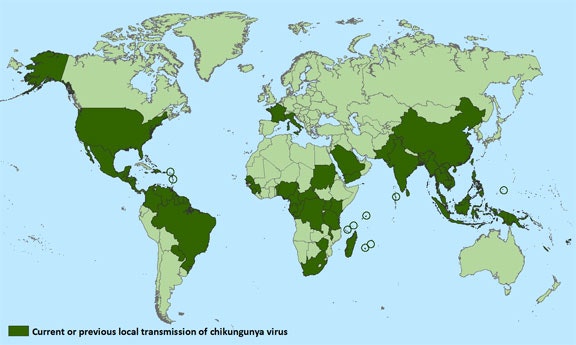
- Chikungunya is a viral disease that is transmitted to people by mosquitoes
- It has occurred in Africa, Southern Europe, Southeast Asia, and islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans
- In late 2013, chikungunya was found for the first time in the Americas on islands in the Caribbean
The mosquitoes
- Aedes species mosquitoes transmit chikungunya virus
- These same types of mosquitoes transmit dengue virus
- These mosquitoes bite mostly during the daytime
Symptoms
- Symptoms usually begin 3‒7 days after being bitten by an infected mosquito
- The most common symptoms are fever and severe joint pains, often in the hands and feet
- Other symptoms may include headache, muscle pain, joint swelling, or rash
Testing
- See your doctor if you think you or a family member might have chikungunya
- Your doctor may order blood tests to look for signs of chikungunya or other similar diseases
